Why Interest Rate Differentials Drive Forex Markets
If you've ever been curious about what causes currency prices to fluctuate, here's one significant indicator – interest rate differentials. Interest rate differentials is simply the difference in interest rates of two countries and is a significant contributor to forex price movements.
Consider it this way - If you could borrow from a friend at 1%, but invest the money in a safe place that pays 5%, you would likely do that deal. In the forex market, there is no borrowing or lending per say, traders are buying and selling currencies based on a differential in interest rates.
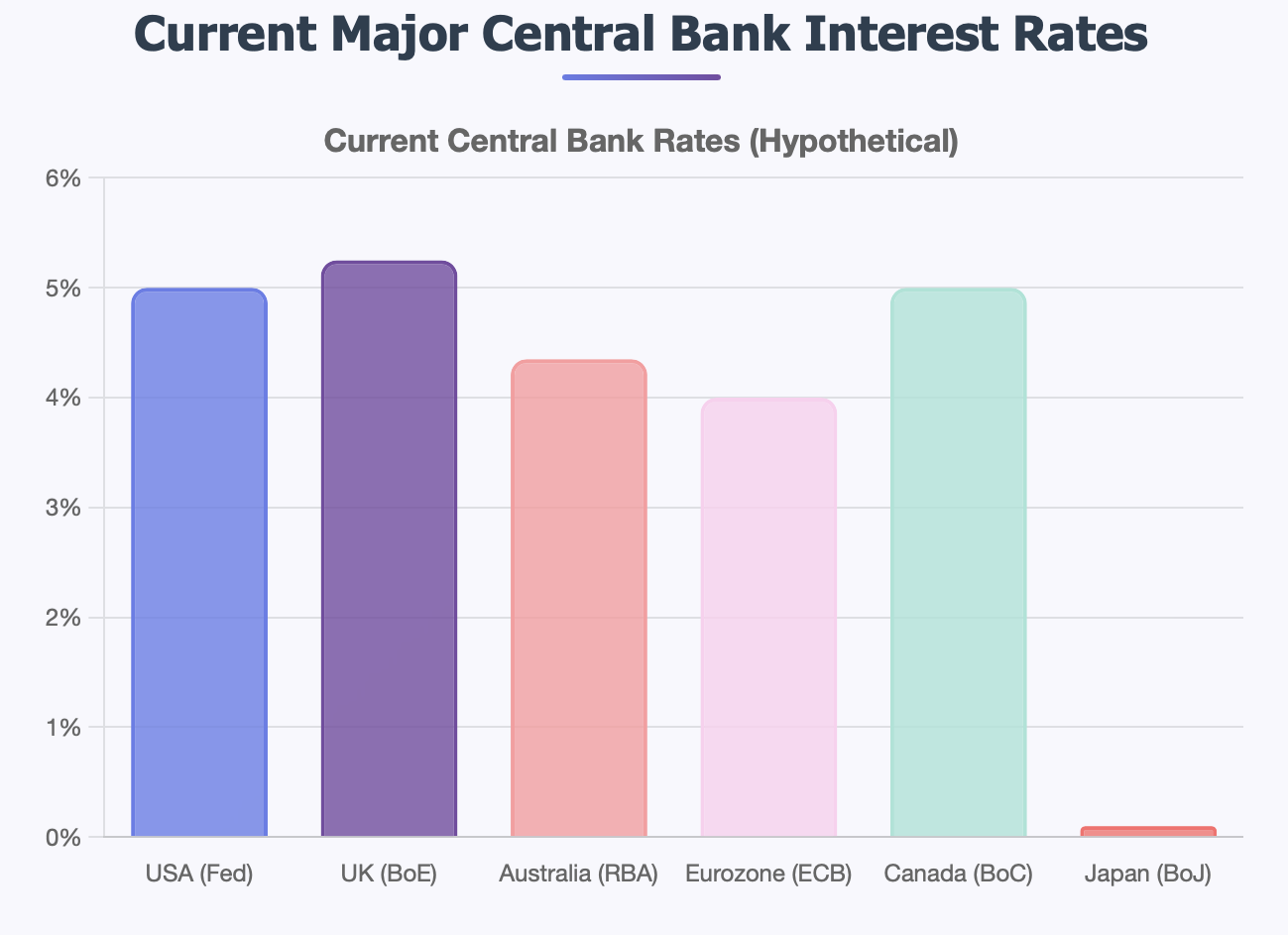
Let's get practical with a real-world example. Let's say the U.S. Federal Reserve has rates pegged at 5%, while the central bank of Japan has it pegged at just 0.1%. This means there is a 4.9% differential. Traders would jump at the chance to profit from that differential, and probably push dollar buying in relation to yen.
The great thing about interest rate differentials is they shed light onto why certain currency pairs move like they do. Typically when you see USD/JPY climb back-to-back over a few months, you usually are looking at bigger interesting rate gap/start to gain, and then repeat.
What Is Interest Rate Differential and How Does It Work?
An interest rate differential (IRD) is precisely as it sounds: the difference between the interest rates set by the two central banks of two countries. The computation is fairly simple, as you take one country's interest rate and subtract the other country's interest rate.
So, what does this mean in practice? If the Fed is at 5%, and the Bank of Japan is at 0.1%, then the USD/JPY interest rate differential is 4.9%. This difference is what traders call a "rate spread".
Why is this important? Because traders prefer to use capital in currencies that have a better positive return. They often need to borrow the low interest rate, i.e., Japanese yen, and use the cash to buy a currency that has a better yield, i.e., U.S. dollar. The constant flow of money going into high rate and out of low rate currencies is what creates prolonged price moves.
Think of the difference like you are choosing between two savings accounts. You may have the option to use Bank A that pays 1% interest while you have an option to earn 5% with Bank B. Assuming no fees, you will choose Bank B. Currency traders always make semi-same decisions, except their comparison is between two NATIONAL economies and not two banks.
The more significant the differential, the bigger possible price movement. A 0.5% differential creates mild pressure and a 4% differential has potential for massive length lasting several months if not longer.
The road from interest rate differentials to macroeconomics
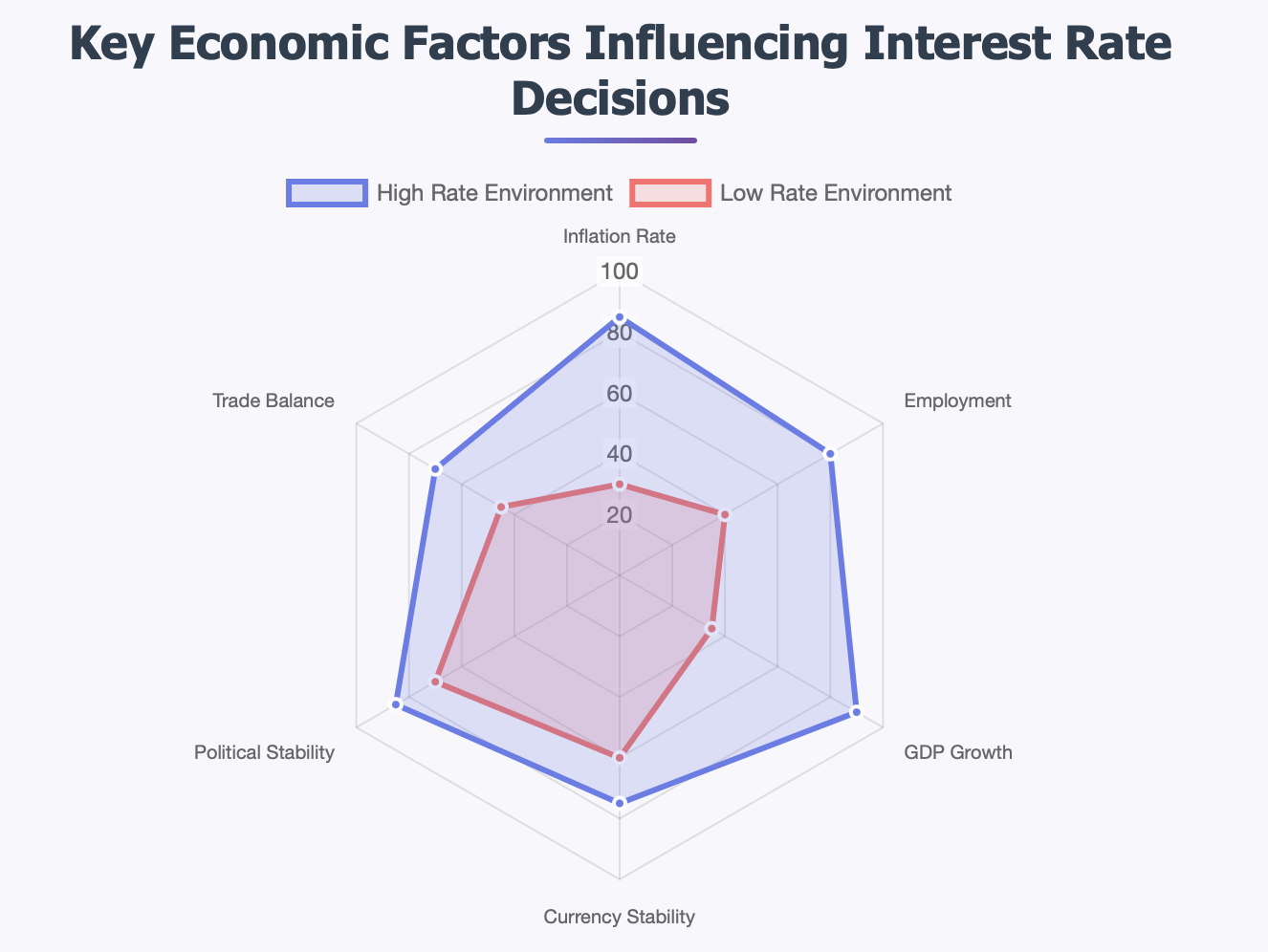
Interest rate differentials do not occur in a vacuum. Interest rate differentials are guided by the economic state of entire countries and the choices of their policy makers. They give us insight on some of the larger macroeconomic trends.
Inflation, for example, will have a large impact in this. When there is inflation in a country, the central bank is likely to keep a close eye on that inflation level and will likely try to cool that inflation with an interest rate increase. In contrast, if there is low inflation in a country, the central bank might decrease interest rate or at least leave it the same creating the differential or widening the differential against their currency pair.
For forex traders, the central bank rate meeting is like a scheduled earthquake. The Fed rates hikes, European central bank holds steady, you usually see a rapid fall off in EURUSD as the market rushes the higher yielding Dollar.
Employment data usually follows the same path. Job growth will usually lead to rate hikes, unemployment rate will lead to rate cuts, and then there is economic growth which typically follows the same pathway, where growing countries have typically higher interest rates than underperforming countries.
The 2020-2022 scenario really illustrates this. During the period, the U.S. economy was on a much quicker growth trajectory than the areas covered by the ECB so the Federal Reserve raised rates aggressively, while the ECB adopted a less aggressive approach. This widening differential ultimately increased the dollar to multi-decade highs against the euro.
When you start to understand the connections, it allows traders to think about where differentials might go rather than just reacting to existing spreads.
Forex Trading Strategies based off Interest Rate Differentials
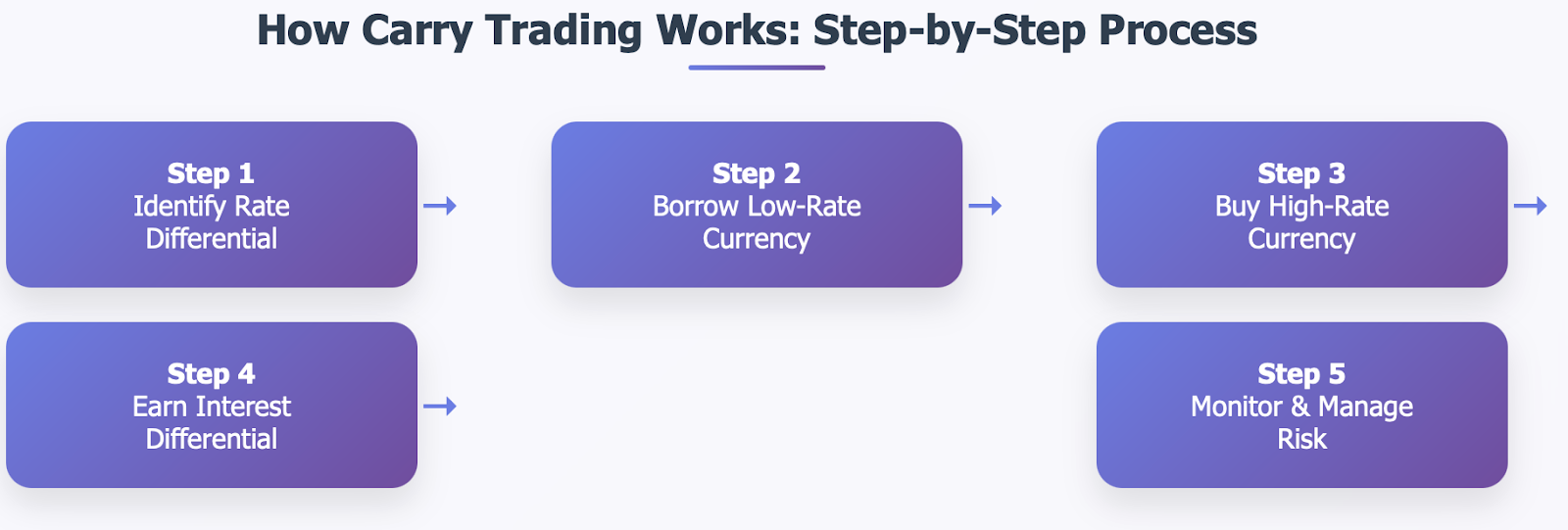
The most well known strategy based on interest rate differentials is the carry trade. The carry trade works as follows, borrow money in a currency with lower interest rates and invest those proceeds in a currency with a comparatively higher interest rate. The profit comes from the monthly interest rate differential and if the currency movement is favorable you make a profit on the changes in currency value.
As an example, if I borrow Japanese yen at 0.1 % and I buy crash some Australian dollars that give me yields of 4% I will make roughly 3.9% on the differential alone. If the AUD/JPY pair appreciates in my favour during that period, the returns are multiplied quite significantly.
Short term traders typically take a different approach. They will follow central bank policy announcements, economic data releases or policy speeches looking for signals indicating future changes to rates, they might then jump into a trade on a build-up of information surrounding the policy. For example a hawkish Fed governor speaking about continued potential to raise rates may result in unexpected USD buying immediately, even before any rate change.
Investors with long-term perspectives prefer stable, unchanging differentials since they are not watching for quick hits of speculative profits on rates but rather currencies with appealing yields and a degree of stability.
The distinction between the two approaches is largely concerned with time period and risk tolerance. Carry traders may hold months or longer, with the assurance that they are earning interest daily in one currency or another while watching the price fluctuate. News traders will often open and close their position on the same day or shift in/out throughout the day to catch very brief movements prompted by a surprise in policy rates.
When you propose differentials as a basis for a trading strategy, position size becomes critical. You will almost always be proposing a leveraged currency trade, where the size of your position can create huge losses with small adverse movements.
Historical Case Studies: When Interest Rate Differentials Shaped Forex Markets
The history of interest rate movement is packed with points where interest rate differentials showed their influence in Forex trading.
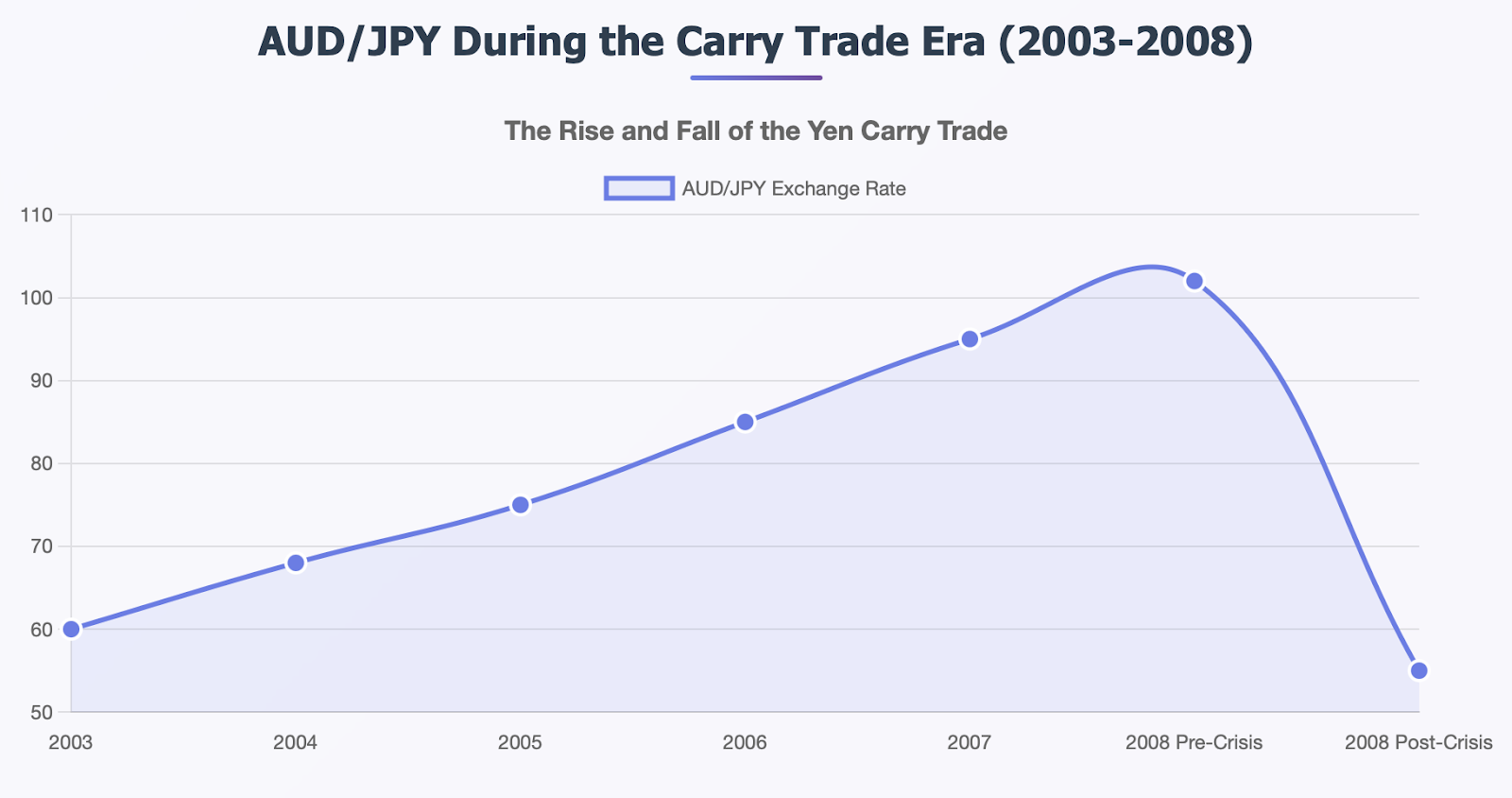
For a historical case, the beginning of the yen carry trade in the early 2000s provides an excellent learning example of the upside and downside of trading on rate differentials. With Japan keeping their rates near 0% while Australia and New Zealand were offering a 5-7% yield, traders were borrowing massive amounts of yen by selling it short to purchase the higher yield.
For many years, everything was great. The AUD/JPY market traded from approximately 60 to over 100, providing both interest income and capital appreciation for carry traders. New Zealand dollars, Brazilian reals, and other high-yield currencies became the darling of forex.
Then along came 2008.
As the global financial crisis began to unfold, investors in full panic mode rushed to unwind their carry trades. They needed to buy yen back to pay off their loans, vastly increasing demand for the yen. The AUD/JPY fell from over 100 to below 55 in a matter of mere months, erasing several years of capital gains and some.
The important lesson is not that carry trades don’t work, rather it is that they work until they don’t. In periods of calm and low volatility, interest rate differential will methodically produce underlying trends, and profits. However, in periods of fear, those same interest rate differential can lead to massive reversals, as traders unwind their leveraged positions on mass.
More recent examples include the move of the dollar in 2022-2023, where the Fed hiked rates faster than every other major central bank, and the weakening of the yen as Japan remained ultra-low while every other country tightened rates.
Risk Management in Interest Rate Differential Trading
Trading interest rate differentials can be rewarding, but it requires sound risk management. The collapse of the carry trade in 2008 was a grim reminder of what can happen if traders do not mitigate their downside risk.
Additionally, stop-loss orders can go a long way to protect capital. Establishing stop-losses at limits that reduce losses to amounts you can live with (2-3% of trading capital for each position), ensures that no single trade can destroy your account.
Moreover, position sizing is more important with differential trades as they usually consist of some leverage and involve borrowed money. Many professional traders, regardless of the attractiveness of a spread, limit their risk to 1-2% of their account on any trade that is based on differentials.
Also, it is wise to diversify your risk. Rather than taking all of your money and putting it into one high-yielding currency, make sure you will be investing across various pairs and time horizons so that a problem with one central bank policy or a country's economy does not destroy your strategy.
Hedging instruments, including forwards and options, can protect against sudden reversals in price, but they eat into your profit and cost a premium. View these instruments as insurance: you hope to not have to use the instrument, however, if you need it, you will be glad you had it.
Also, consider correlation risk. Many of the high-yield currencies also tend to move together during risk-off periods, which means that what may appear to be diversification will not provide as much protection as expected.
Geopolitical Events and Interest Rate Differentials
Wars, pandemics, and financial crises can upend well-thought-out differential trades in seconds. These events reduce central banks' capacity to follow their policy frameworks and force them to redefine priorities in ways that can result in very different interest rate definitions.
The global COVID-19 pandemic is illustrative. In March 2020, central banks around the world lowered rates to near zero percent. The scale of these actions immediately eliminated many of the interest rate differentials from which trading in forex could induce trends. Carry trades that had worked for many months became instantly unprofitable, as billions of dollars' worth of agency vanished with the rate gaps.
The Russia-Ukraine conflict has created different avenues of disruption. Energy prices across Europe rose rapidly, putting the European Central Bank in the situation of balancing concerns of inflation (prompted by rising energy costs) with declines in economic growth. Meanwhile, the Fed continued hiking rates, creating another opportunity to introduce differentials in the EUR/USD.
Political uncertainty is also important to watch. Brexit deliberations continuously moved GBP rates and GBP differentials because market participants attempted to price the economic ramifications of the different scenarios. Elections, policy changes, leadership changes, and the changing profile of central bank governors can create changes in the fortunes of interest rate spreads.
The important takeaway for traders is that geopolitical events can supersede economic fundamentals. A currency can offer a great yield, but if political risk threatens the security of the country, the yield may not be worth the risk.
You should stay on top of events around the world, and think about how they may influence monetary policy series. A differential trade in currency may be best if you recognize that external risks are too significant to take a position.
Back to my earlier topic: The Future-Where Are the Differential Headed?
Looking ahead, several trends are likely to influence interest rate differentials in the near future. The Federal Reserve seems committed to higher interest rates until inflation returns to their 2% target and Japan seems reluctant to raise and raise rates even though they recently made some policy shifts.
If the above holds, it implies that USD/JPY differentials may remain wide which would support dollar strength against the yen. However, keep an eye on signs that inflationary pressures in Japan forces the Bank of Japan to rethink their ultra-accommodative policies.
In Europe, the picture is more complicated. The ECB has aggressively raised rates from previous lows, but the weakness in the eurozone could limit further hikes. If the U.S. economy is stronger than Europe, then EUR/USD differentials can keep benefitting the dollar.
Emerging markets currencies can provide attractive differentials, notwithstanding the added political and economic risk. Brazil, Mexico, and Turkey are examples of countries that provide large spreads, with currency changes often offsetting the differential gains.
Watch inflation trends around the globe. If inflation pressure remains stubbornly high on one side of the globe while easing on another, new differential opportunities will begin to develop. Countries that defeat inflation soonest will have their central banks lower rates first, thereby offering whole new trading opportunities.
Central bank communications are changing. Policy makers are becoming more open about their positioning, and informed traders can see potential rates change and differential moves on the horizon.
Some Key Takeaways for Forex Traders
Interest rate differentials provide excellent trading opportunity, with serious risks. They can create sustained trends for several months or even years but can reverse violently with shifted market conditions.
The most critical takeaway is that opportunity and risk are inseparable. High differentials might translate to higher potential profits, but it typically means greater volatility and risk to the downside as well.
As a new trader, staying on top of major central bank meetings and policy announcements will provide an understanding of what influences rate decisions, and it will allow you to anticipate changes in differentials before they actually occur. Always use stop-loss orders, especially for the larger trades, and never risk more capital than you can afford to lose on a single trade.
Diversification over a number of currency pairs and time frames can help to reduce risk while providing an opportunity to capture differentials. Regardless of how appealing it may look, never utilize all of your trading capital for one carry trade.
Synched trading capital gives you diversification opportunities, but it's important in contributing to your overall trading solutions portfolio.
And finally, all previous meetings aside, keep in mind that interest rate differentials are but one variable impacting currency prices. There's a plethora of factors that can come into play that can trump any trends driven by differentials, including, interest rate volatile events, economic data, and market sentiment. Also, many other things occurring globally that we don't even hear about - or only hear anecdotal don't forget about them either!
Are you ready to trade forex with confidence? Our purpose is to help traders like you with educational tools, timely market analysis, and real-life operational experience to practice interest rate differential strategies with the thousands of successful traders at BTCDana.
Start your trading education journey now, and take advantage of what the market offers you and turn the opportunities into profits.