Introduction: Why Risk Management Is the Core of Forex Trading
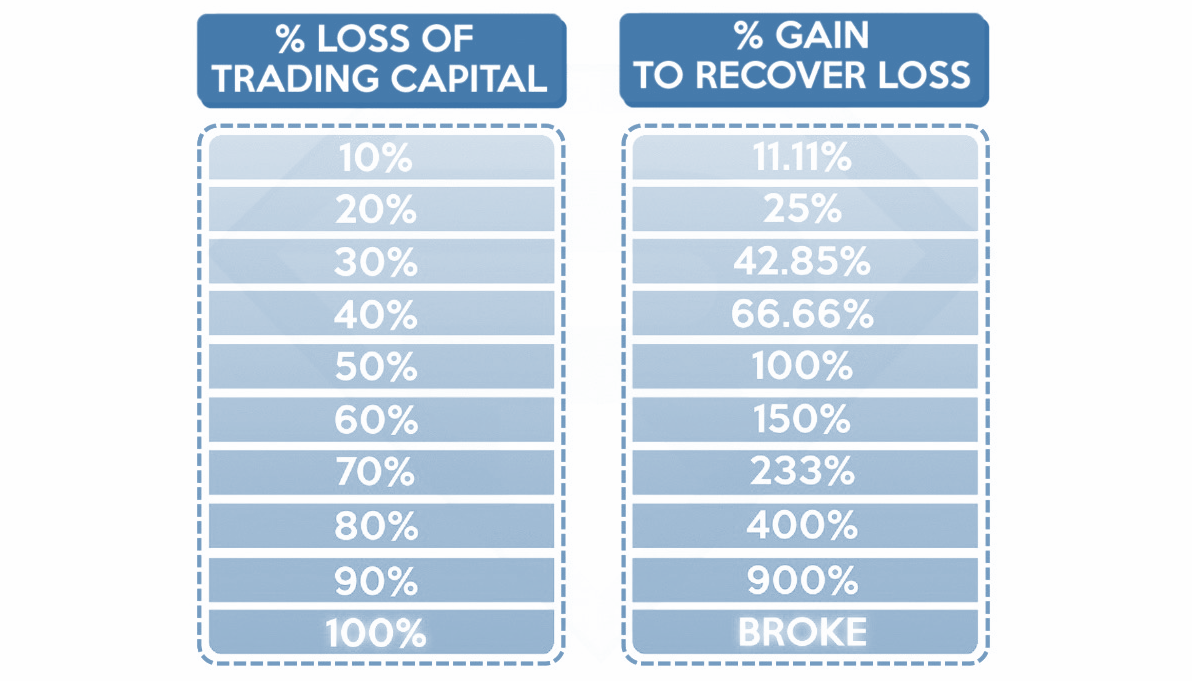
Risk control is the basis of any successful trading strategy. The goal of forex risk management is capital protection and surviving market volatility. To put it simply, trading without a risk control strategy is like gambling. By figuring out and limiting how much you're risking before every trade, you keep control. If you lose 50% of your account, you’d need to gain 100% just to get back to where you started. Risk management ensures you can “live to trade another day” by avoiding a sudden Game Over in your trading account.
-
Common beginner mistakes: risking the entire account on one trade, trading with no stop-loss, or recklessly adding to losing positions can lead to big trouble.
Think of stops and limits as your “extra lives.” They let you take a loss without losing the whole game. Trading without these measures is just taking chances. You need to plan for losses just as much as for profits.
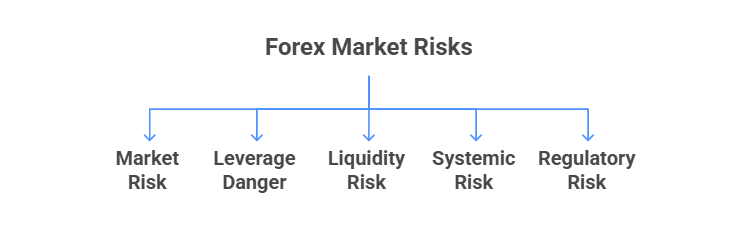
Types of Forex Market Risks
Before you get into risk management, you have to understand the dangers and different types of trading risk in forex:
-
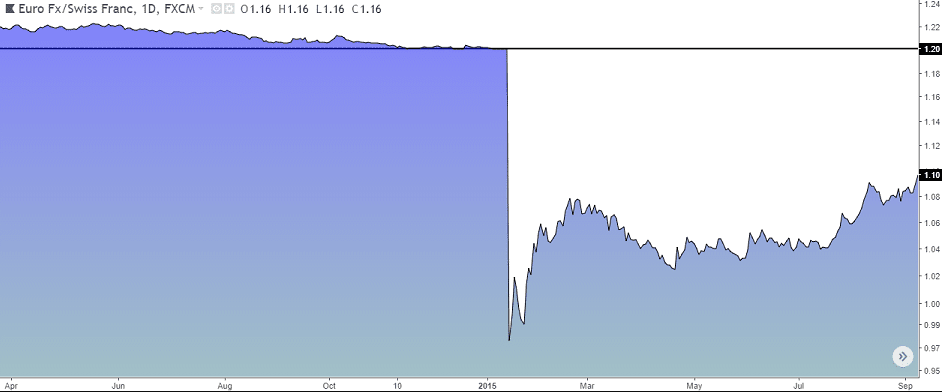
Market Risk: This is the danger of price swings. Currency rates change all the time due to news, economic updates, or central bank moves. For instance, when the Swiss National Bank suddenly dropped the EUR/CHF peg, it caused the EUR/CHF to drop almost 30% in just minutes.
-
Leverage Danger: Forex often uses high leverage (borrowing). Leverage magnifies both gains and losses. A 1% price move on a 100:1 leveraged trade equals 100% of your stake. Going too far with leverage can blow up your account, while not using enough means you're leaving money on the table.
-
Liquidity Risk: Liquidity is the ease of buying/selling. In low-liquidity conditions, even small orders can create large price gaps and slippage. For example, placing a market order during an illiquid period might fill at a much worse price than expected. Wide spreads and failed fills are symptoms of liquidity risk.
-
Systemic Risk: This covers unpredictable failures in the system – e.g., platform outages, data-feed glitches, or flash crashes. If your broker’s platform goes down during a spike, you may be unable to exit a position at any price. The 2015 SNB event also had elements of systemic risk: some brokers collapsed under client losses.
-
Regulatory Risk: Policy changes or broker issues can constrain trading. New capital requirements, trading bans, or a broker losing its license can force sudden account changes or liquidations.
These forex market risks are serious. You need to recognize both the downsides and the upsides when trading. The first step to managing risk successfully is understanding these different types of risks.
Strategy 1: Set Stop-Loss and Take-Profit
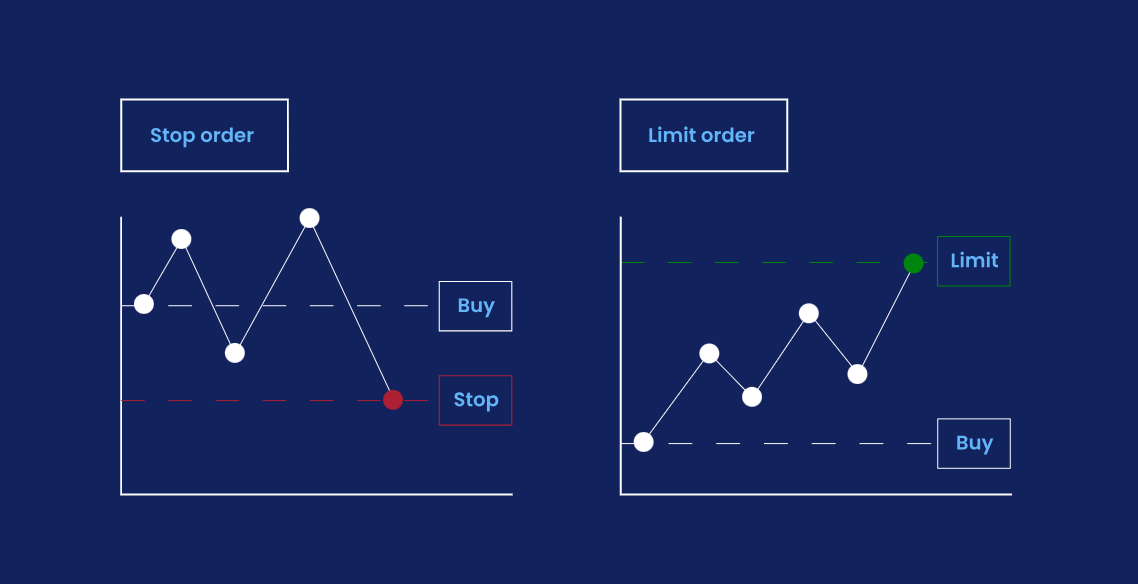
One of the simplest and most effective risk control techniques to protect your capital is by setting stop-loss and take-profit orders. A stop-loss order (S/L) automatically closes your position when the price hits a certain point, limiting potential losses. A take-profit plan (T/P) locks in your gains by closing your position when the price reaches a set level.
To set them effectively, you can use methods like:
-
Support/Resistance Levels: Set your stop-loss below support levels and take-profit at resistance.
-
ATR (Average True Range): A more dynamic method that adjusts stop-loss and take-profit based on market volatility.
-
Fixed %/Pips: Some traders risk a set % of equity (e.g., 1–2%) or fixed pip distance. While simple, fixed stops must still allow for market swings.
Don’t make these mistakes:
-
Setting stop-loss orders too tight can lead to being stopped out prematurely.
-
Setting them too wide exposes your account to excessive losses.
-
Moving your stop-loss constantly to avoid accepting a loss.
It's like setting a timer for your exam. Don’t get stuck on one question; move on when you have to. Basically, having a solid stop-loss strategy means that one bad trade won’t wipe out your account. They’re your first line of defense.
Strategy 2: Position Sizing & Capital Allocation
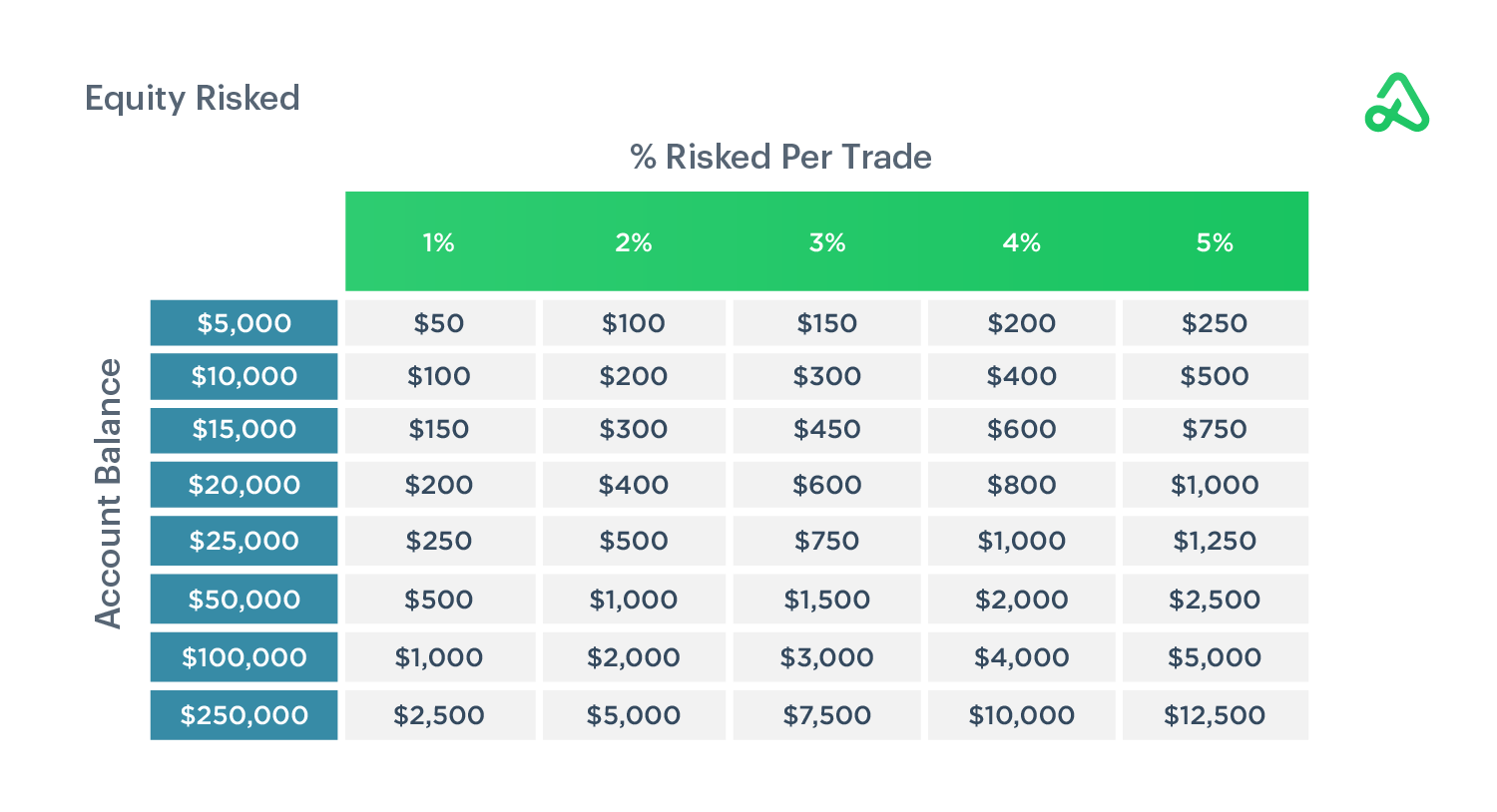
How much to trade is as important as what to trade. Position sizing means choosing how large a trade to take given your account size and risk tolerance. The goal is to risk only a small fraction of your capital on each trade. A common capital allocation rule is the 1%–2% rule: never risk more than 1–2% of your total equity on a single trade.
Some traders use more formal models like the Kelly Criterion to figure out an “ideal” risk percentage based on how often they win and the odds. The main thing is to be consistent: pick your percentage (whether it’s fixed or based on volatility) and stick to it.
Why sizing matters: With high leverage, making a few big bets can ruin your account even if you’re right 90% of the time. Taking on too much risk (big positions) can really increase your losses.
-
Downsides of oversizing: more margin calls, increased stress, and a really short buffer. Just one surprise move can lead to disaster. In extreme situations (like the 2015 Swiss shock), many brokers shut down positions when clients ran out of margin.
-
Downsides of under-sizing: slow growth and boredom. You might double your account but still feel like you’re not making progress because each trade barely moves the needle.
Think of your account like chips in a game: don’t bet your last token. Using a fixed percentage rule or adjusting based on volatility means you can handle even a losing streak. Position sizing is literally the lifeline of your trading account.
Advanced Tools: Hedging, Pending Orders, and Exposure Control
Beyond just basic stops and sizing, pro traders use advanced tools to manage risk and exposure in ways that keep them ahead of market ups and downs:
-
Forex Hedging: A hedge is when you take a position that moves in the opposite direction of your main trade. For example, if you’re short USD (expecting dollar weakness), you might buy gold (which often rises when USD falls) to reduce net risk. Essentially, you are spreading exposure.
-
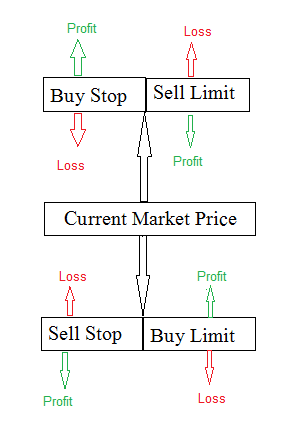
Pending Order Setup: These are entry orders to catch breakouts or pullbacks automatically. A buy-stop order, for instance, will only execute your buy when price rises to a set point. A sell-limit order sets an entry if price falls to a certain level. Use these to enter trades at precise levels without watching 24/5, and to pre-commit to risk levels.
-
Dynamic exposure control: As your account grows or the market changes, adjust your position size and risk accordingly. For example, if your account doubles, you might trade slightly larger sizes while keeping your risk percentage the same.
These tools are like extra protection: they won't stop all losses, but they help you manage and limit how much risk you take on at each step. Good risk management is all about having layered, structured defences.
Black Swan Forex Events: Risks in Extreme Situations
“Black swans” are rare, unpredictable shocks that send markets haywire. Examples include the 2015 Swiss Franc decoupling, Brexit vote, or the COVID-19 crash. In these events, volatility explodes, and normal risk limits can be overwhelmed. A forex flash crash can wipe out accounts in seconds. To manage crisis risk control, you must prepare:
-
Extra Margin: Keep additional margin in your account to prevent a margin call during extreme events.
-
Limit Orders: Set limit orders before a potential event to secure exits at reasonable prices.
-
Guaranteed Stop Loss: Use brokers who offer guaranteed stop-loss orders to protect against sudden price moves.
For example, when SNB dumped the EUR/CHF peg in Jan 2015, the franc surged 30% immediately. Many traders who didn’t set stop-losses ended up losing a lot. Some brokers faced client losses they couldn’t handle, leading to bankruptcies. The takeaway? Extreme volatility will happen. So, be ready with extra margin, strict stops, and a cool head.
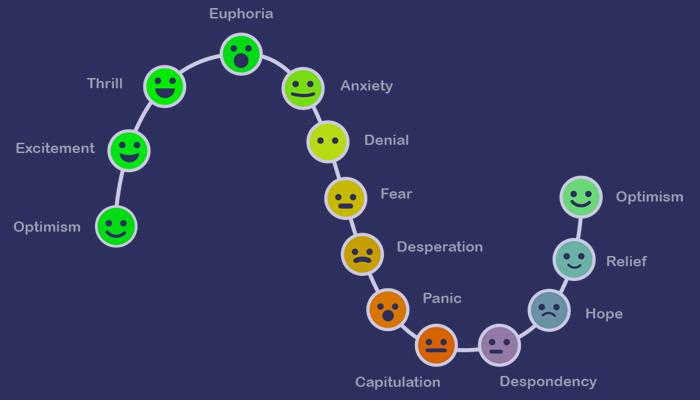
Trading Psychology: Managing Emotional Risk
Even if you have a perfect trading strategy, your mind-set can make or break you. Emotional risk control is your final layer of defence. Feelings like fear, greed, anxiety, or revenge trading can erase a rational plan. Always stick to your set rules, not your impulses.
-
Set personal limits: Some traders set a daily loss limit. For example, if you lose 2% of your account in one day, stop trading for that day.
-
Journaling and review: Keep a journal of your trades and how you felt during them. Look back regularly to spot trends. Studies show that systematic review improves discipline in trading.
-
Take breaks: If you’re upset or overconfident, take a pause.
Just like in basketball, you shouldn't carry the frustration of a loss into the next game. In trading, you need to keep greed and fear in check. Remember, your mindset is the last hurdle in controlling risk.
Case Study: One Success, One Failure
Let’s compare two trading case studies to see risk control in action:
-
Winning Trade (Good Risk Control): Alice identifies a bullish EUR/USD trend and risks only 1% of her account. She enters in two steps—part at the market and part on a pullback—and sets a stop-loss below the recent swing low. Her take-profit is placed at resistance. As price moves up, she shifts her stop to break-even, then higher to lock in gains. Alice’s trade reflects a winning forex strategy grounded in planning and discipline, and she earns a 2:1 reward-to-risk win.
-
Losing Trade (Poor Risk Control): Bob bets big on NZD/USD, risking over 10% of his account with no stop-loss. When a news event reverses the market, he quickly takes heavy losses. Instead of exiting, he adds more to average down, hoping for a rebound. The market keeps falling, and by the time he exits manually, his account is nearly wiped out. This is a textbook case of stop-loss failure and emotional trading.
The main difference wasn't who was “right” about market direction, but whose risk management was solid. Trading isn’t just about being smart or lucky; it’s about having a systematic approach.
Practical Risk Management Checklist (SOP)
Make risk control systematic by turning it into a checklist or SOP:
Treat this risk checklist like a pre-flight drill – a systematic forex SOP keeps emotions out of critical risk decisions.
Conclusion
Effective risk management is non-negotiable in forex. It's not about getting rid of all risk (which is impossible) but finding the right balance between risk and reward. Protecting your capital is the first step to long-term success. Start putting strong risk controls in place today.
Every successful trader’s motto is “Trade to survive”, not “Trade to always be right.”
BTCDana offers a free demo trading platform where you can apply stops, position sizing, and hedging without risking real money. By building good habits now – cutting losses, sizing trades, and staying disciplined – you ensure that your trading career can grow steadily.
With disciplined risk management, you’ll learn and make profits without risking your future. Trade safely, trade smart, and keep your account healthy.