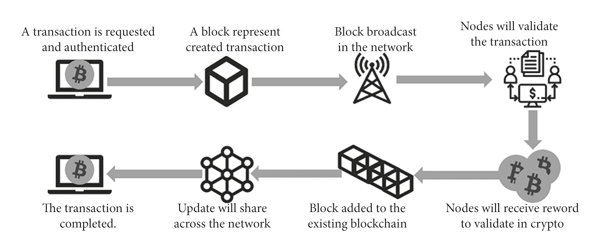
1. Introduction: The Intersection of Crypto and AML
Digital currencies have swiftly transformed from a specialized technology to a fundamental element of worldwide financial advancement. Presently, virtual assets such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, and stablecoins are utilized, stored, and exchanged by millions—especially in developing regions across Southeast Asia, Africa, and Latin America. With a focus on mobile accessibility, the allure lies in rapid transactions, decentralization, and enhanced financial inclusion.
Nonetheless, these same characteristics—anonymity, decentralization, and seamless transactions across borders—lead to significant compliance challenges. In the absence of centralized regulation, cryptocurrency platforms have become prime targets for the laundering of illegal funds, financing of terrorism, and tax evasion. According to Chainalysis, more than $24.2 billion in illegal funds were transacted through cryptocurrency in 2023 alone, despite strides in regulation.
In reaction, regulators around the globe are intensifying enforcement measures. From the FATF’s international crypto AML protocols to domestic crackdowns, authorities are signaling that cryptocurrency companies must adhere to the same regulations as conventional financial entities. Fines have soared into the hundreds of millions, and in certain instances, criminal charges have followed.
To foster trust and sustain long-term development, the cryptocurrency sector must adopt compliance measures. This article delves into global AML regulations, essential compliance strategies, their operational implications for exchanges and users, best practices, and future developments influencing digital currency regulation.
2. Overview of Global AML Regulations
Global AML regulations aim to identify and prevent the concealment of illegal financial activities. For cryptocurrencies, this has emerged as a worldwide priority as regulators strive to bridge gaps in the financial system.
International Oversight Bodies
-
FATF (Financial Action Task Force): Establishes worldwide AML benchmarks. Its 2019 recommendations introduced AML protocols for cryptocurrencies and the “Travel Rule,” requiring data sharing on cryptocurrency transactions exceeding $1,000.
-
United Nations: Collaborates with national governments to combat the financing of terrorism, particularly in relation to virtual assets.
-
OECD (via CARF): Creating global frameworks for cryptocurrency tax transparency—aligned with AML objectives.
National Regulations Snapshot
Emerging Trends
-
CASP Registration: Numerous countries now mandate that cryptocurrency platforms register as Crypto Asset Service Providers (CASPs).
-
FATF Warnings: Several nations have faced public reprimands for not fulfilling cryptocurrency AML responsibilities.
3. Core AML Elements in Cryptocurrency
To comply with global blockchain AML mandates, cryptocurrency companies must incorporate both conventional compliance measures and blockchain-specific strategies.
Key Operational Measures
-
KYC (Know Your Customer): Compulsory identity verification utilizing government-issued documents and biometric technology.
-
Transaction Monitoring: Platforms deploy algorithms to identify suspicious trading patterns or transfers.
-
On-Chain Analytics: Tools like Chainalysis track wallet histories and highlight blacklisted addresses.
-
Blacklist Filtering: Screening addresses against sanctions lists (e.g., OFAC, UN).
-
Transparency Audits: Conducted both on-chain (wallet activities) and off-chain (internal documentation).
-
AI-Driven Compliance Tools: Automation enhances efficiency and minimizes false positives.
-
Fund Segregation: A regulatory necessity in regions like Singapore—ensures that customer funds are securely stored in cold wallets.
4. Impact of Global AML Laws on Crypto Exchanges and Users
AML regulations transform the operations of crypto platforms—and have a direct influence on user experience.
Operational Impact on Exchanges
-
Mandatory Comprehensive KYC: Prolongs the onboarding process and requires user documentation.
-
Increased Compliance Costs: Smaller exchanges struggle to handle staffing, technology, and audits, with crypto compliance cost becoming a critical barrier to entry and sustainability.
-
Cross-Border Issues: Jurisdictional conflicts may obstruct transactions or require licensing in multiple areas.
User-Level Impact
-
Reduced Privacy: Traders must disclose their identities and sometimes the reasons for their transactions.
-
Account Suspensions: Transfers linked to unverified wallets can result in account freezes.
-
Obstacles in Accessing DeFi: Decentralized platforms face challenges enforcing AML, which may attract regulatory scrutiny.
Benefits for Long-Term Users
-
Improved Security: More secure platforms with diminished fraud risks.
-
Regulatory Clarity: Easier tax reporting and asset verification in developing regions.
5. Best Practices for Cryptocurrencies to Comply with AML
Both platforms and traders can actively improve their compliance readiness. Here’s how:
For Crypto Platforms
-
Establish internal AML policies in line with FATF and national regulations to form the core of a scalable blockchain compliance strategy.
-
Utilize multi-tiered KYC tools that include biometric and document verification
-
Incorporate both off-chain (manual assessments) and on-chain analysis
-
Conduct regular audits of compliance systems
-
Collaborate with blockchain analytics firms
-
Provide ongoing AML training and certification for staff
-
Report suspicious activities and work with regulators
For the Broader Industry
-
Advocate for self-regulation through trade associations
-
Support open-source compliance tools
-
Share AML processes in transparency reports
6. Future Trends in Crypto AML Compliance
The landscape of crypto compliance is rapidly changing. Here’s what’s on the horizon:
Key Developments
-
Global Standardization: FATF and OECD continue to push for harmonized AML regulations, forming the basis for global crypto regulation development and reducing jurisdictional discrepancies that can hinder international operations.
-
AI & Big Data: Quick adoption of RegTech to forecast, identify, and thwart laundering activities
-
DeFi & NFT Regulation: AML regulations could extend to smart contracts and NFT platforms
-
Cross-Border Data Exchange: OECD’s Crypto-Asset Reporting Framework (CARF) requires automatic data sharing
-
Emergence of CBDCs: As central banks introduce digital currencies, interoperability with AML-compliant crypto platforms will be essential
7. Conclusion: Compliance as a Pillar for Healthy Crypto Markets
AML compliance is not merely about regulations—it’s essential for market sustainability, investor protection, and long-term credibility. The importance of crypto compliance grows as digital assets become deeply embedded in global finance, especially across emerging markets and mobile-first economies.
By implementing best practices, adopting technology, and adhering to changing regulations, both exchanges and users can enjoy a more secure and transparent ecosystem. Crypto must adapt to meet global financial standards, particularly as it becomes crucial for international trade, remittances, and digital assets in developing markets.
Call to Action:
Discover btcdana’s compliance resources, download our AML guide, or create a secure trading account designed to align with the latest global standards.