Introduction: What is leverage & why is it important in forex trading?
If you ask folks what differentiates forex trading from stock trading, they will often name leverage as one of the factors. But what is leverage, and why does it matter so much in currency trading?
Leverage is like a financial superpower. It allows you to take on a considerably larger trading position with only a small amount of your own funds at risk. You can think of leverage as borrowed power from your broker or as a way to increase your trading position size considerably with a relatively small amount of your own money.
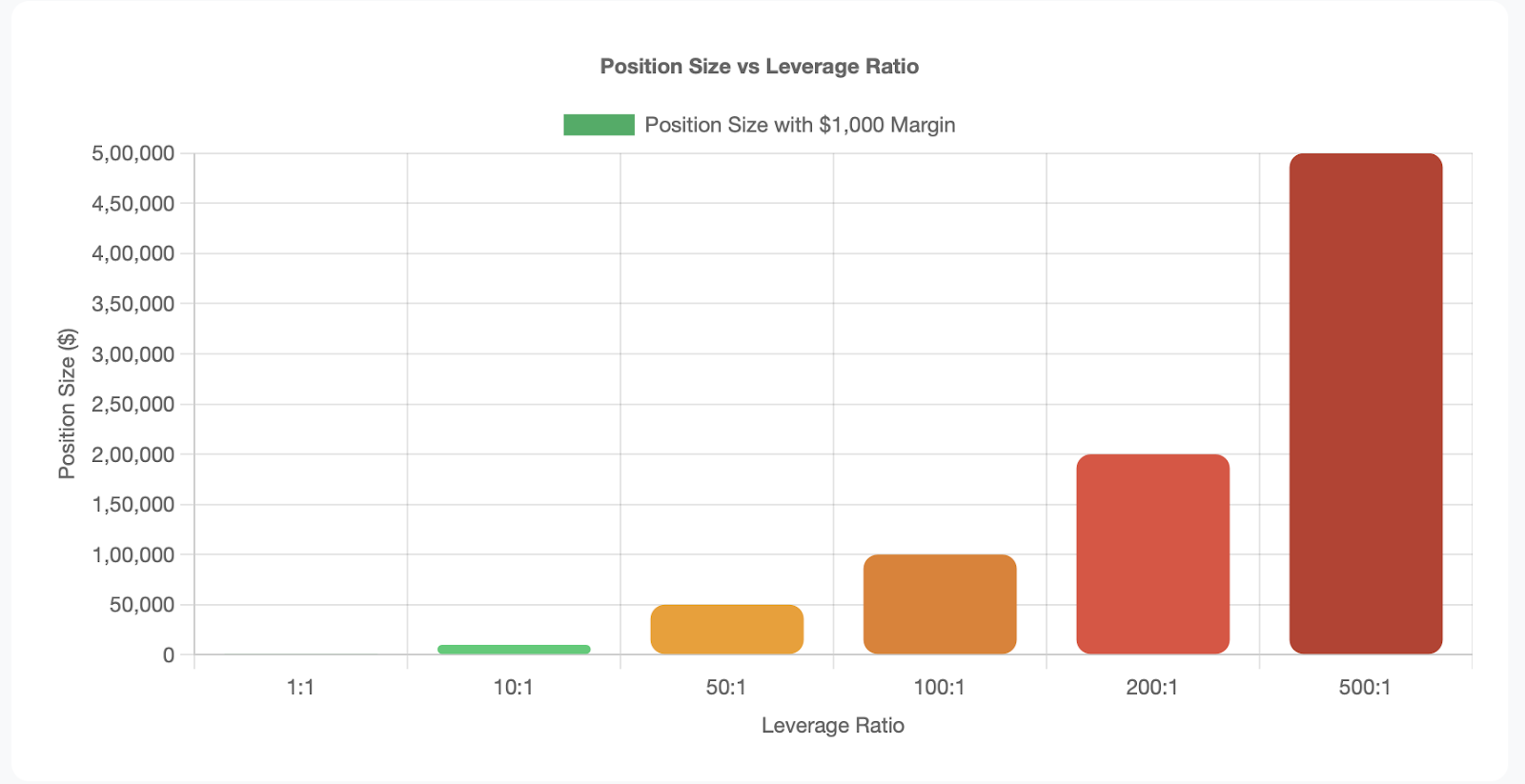
For example, when trading in forex, instead of requiring $100,000 to trade one standard forex lot, you would only need a mortgage of $1000 of your own capital with 100:1 leverage.
Leverage is important in forex trading because currency price movements are typically measured in very small increments, called pips. Without leverage, most retail traders would only make small amounts of profit from small price movements. EUR/USD might only move 50 pips to reap only a couple of dollars of profit without leverage, but with leverage properly employed, that same move might easily yield hundreds of dollars instead.
In terms of leverage, the forex market stands apart from the traditional equity markets. Stock trading accounts generally offer low leverage (usually 2:1 or 4:1), but forex brokers offer leverage of 50:1,100:1, and even 500:1 depending on where you are and the regulatory environment in your region.
However, here is what you need to grasp: Leverage is not good or bad - it is a tool that magnifies your profit potential and your loss potential. Properly used with risk management, leverage can allow you to create wealth faster. Improperly used, it will obliterate your trading account faster than you might think.
In this guide, we will explain how leverage actually works, walk through actual calculations, provide examples, and most importantly, show you how to utilize leverage in a smart way to protect and increase your capital. Even if you are completely new to forex or just want a refresher course, this guide will equip you to make an educated judgement pertaining to leverage on your trading journey.
Definition & How Leverage Actually Works
We will break down leverage into smaller pieces so you can fully understand how it works in forex trading.
The Core Definition
Leverage means multiplying your own capital (called margin) to control a trade size that is greater than the amount in your trading account. Think of it as a loan from your broker and essentially a way to leverage your trading in greater size than your account balance.
The Essential Formula
The simple formula for calculating leverage is:
Trade Size = Your Capital × Leverage Ratio
For Example: $1,000 × 100:1 leverage = $100,000 position size.
This means your $1,000 of money would control a $100,000 position in the forex market.
Understanding Margin
Margin is the deposit you are required to put down for your leveraged position, it is not a fee or a cost - it is basically collateral that gets locked up while your trade is open. The margin requirement is calculated as follows:
Margin Required = Position Size ÷ Leverage Ratio
And our example: $100,000 ÷ 100 = $1,000 margin required.
The Margin Call Fact
Here is where it gets serious. If your trade moves against you towards your margin, and your losses are near your deposit margin, your broker will issue you a margin call, which is a warning that either more funds have to be deposited or you will have to close some of your positions. If this does not happen, the broker will automatically close your positions out, so you cannot lose more than your own account balance. This will be referred to as a stop-out.
Rule Differences
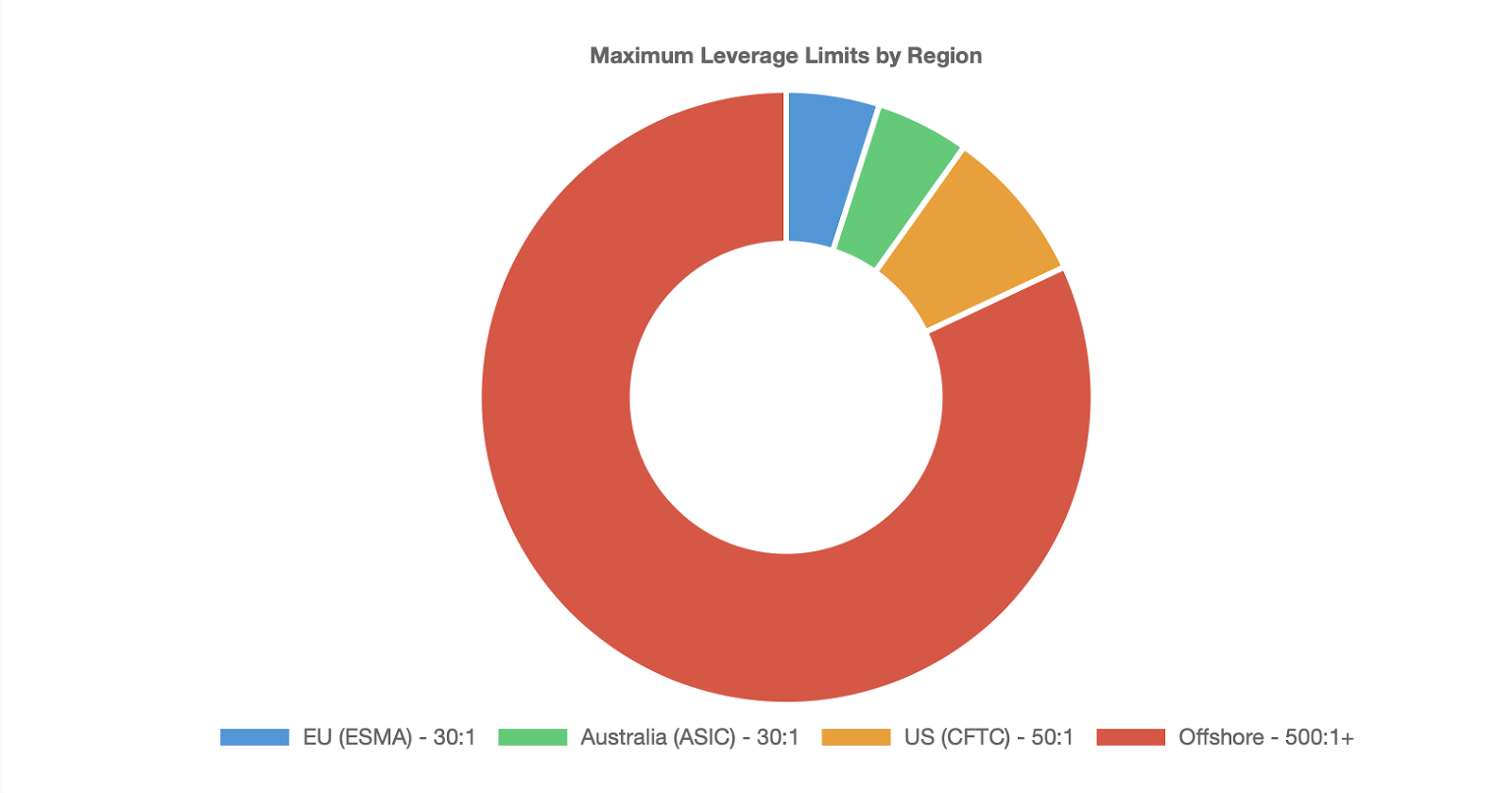
Leverage limits will widely differ depending on where you are located and by which broker regulation is applied:
European potential (ESMA): 30:1 maximum on the major currency pairs
Australia (ASIC): 30:1 maximum for retail clients
United States (CFTC): 50:1 maximum on major pairs.
Offshore brokers can offer 500:1 or higher.
The Amplification Factor
The main idea to take away from this is leverage magnifies everything, in a proportionate manner. If for example, the EUR/USD moves 1% in your favour, and you are using 100:1 leverage then your return is 100% of your margin. If the EUR/USD moves 1% against you then you have lost 100% of your margin.
The Reality of Position Sizing
When you use leverage you aren't just increasing your profit potential, you are also increasing your exposure to the risks of the market. A standard lot in forex is 100,000 units of the base currency. Without leverage, you would need the full base currency value of $100,000 to trade one standard lot of EUR/USD. With 100:1 leverage, you would only be required to have $1,000, but you'd still be taking the full risk of a $100,000 position.
That's the breakdown of why professional traders constantly say that higher leverage does not mean higher profits - it means that you need to be more precise with your position sizing and risk management in order to cut off the chances of catastrophic losses.
Pro Example: A Forex Leverage Calculation
Let’s go through an entire real-world example to demonstrate how leverage can affect your trading results from beginning to end.
The Setup
Meet Sarah. Sarah has a forex trading account with a balance of $2,000. Sarah wants to trade EUR/USD and is going to trade 100:1 leverage offered by her forex broker.
Now let’s look at how Sarah’s trade plays out step by step.
Step 1: Planning the Trade
Sarah decides to open 1 standard lot (100,000 EUR) of EUR/USD, now let’s do some basic math:
-
Position size: 100,000 EUR
-
Leverage: 100:1
-
Margin required: 100,000 ÷ 100 = 1,000 USD
-
Account balance: $2,000
Free margin, after the trade: $2,000 - $1,000 = $1,000
Step 2: Opening the Trade
Current price of EUR/USD: 1.1000
Sarah opens a long position of EUR/USD (buying EUR, selling USD) at 1.1000, and the broker locks-in the $1,000 for the margin, which leaves Sarah with $1,000 of free margin, in case she makes a loss on this trade, or makes another trade.
Step 3: Learning About Pip Values
For a standard lot of EUR/USD, we know that:
1 pip = 0.0001 price movement
1 pip value = $10 USD
This means that for every pip the market moves, that is also $10 in profit or loss for Sarah's position.
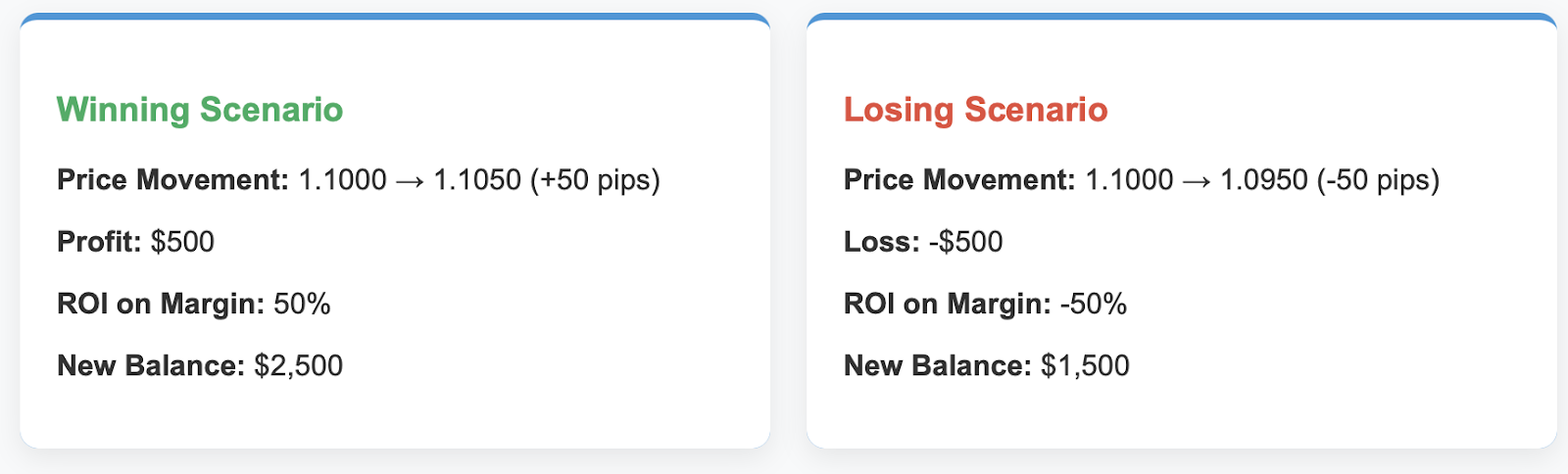
Scenario A: The Winning Trade
The market moves in Sarah's favor, when the EUR/USD rises from 1.1000 to 1.1050 – a total gain of 50 pips.
We can calculate the profit:
-
Pip movement = 50 pips
-
Profit per pip = $10
-
Total profit = 50 × $10 = $500
The ROI (Return on Investment) can be calculated as follows:
-
Initial Margin = $1,000
-
Profit = $500
-
ROI = ($500 ÷ $1,000) × 100 = 50%
At the end of Scenario A, Sarah’s new account balance is $2,000 + $500 = $2,500.
Scenario B: The Losing Trade
So now we can see what if the market moved against Sarah. In Scenario B, the EUR/USD fell from 1.1000 to 1.0950 – a total movement of 50 pips.
We can calculate the loss:
-
Pip movement = -50 pips
-
Loss per pip = $10
-
Total loss = 50 × $10 = $500
We can also calculate the Return on Investment (ROI) like this:
-
Initial Margin = $1,000
-
Loss = $500
-
ROI = (-$500 ÷ $1,000) × 100 = -50%
At the end of Scenario B, Sarah’s new account balance is $2,000 - $500 = $1,500.
The Amplification Reality of Leverage
Remember, a 0.5% move in the currency pair (50 pips of the approximately 11,000 pips in price) equated to a change of approximately 25% to Sarah's total account value. This is what can make leverage both good and bad:
-
Without leverage: If EUR/USD moves 50 pips with a $2,000 position, Sarah would gain or lose about $9
-
With leverage: If EUR/USD moves 50 pips with a 100:1 position, Sarah would gain or lose $500
Risk Management Lesson
If Sarah had not used a stop-loss and EUR/USD fell 200 pips (from 1.0800), she would have had a;
200 pips x $10 = $2,000 loss
She would have wiped out her entire account
This example demonstrates why professional traders never trade using only leverage, rather they enforce gambit rules for risk management, such as stop losses, proper position sizing, and never risking more than 1-2% of their account with a trade.
The important take away message is that leverage amplifies both opportunity and risk in equal weight. Risk management is therefore not just important but is indeed necessary for trading for the long term.
Everyday analogy: leverage made easy for beginners.
Sometimes a familiar, everyday situation provides the best understanding of tricky financial concepts. Let's investigate leverage with these three simple analogies that will clarify this topic for you.
Analogy 1 - The Seesaw Concept
When we were kids on the playground, we'd sometimes play seesaws. Remember when you wanted to lift your heavier friend? You couldn't do it with just your weight. As soon as you scooted back on your side of the seesaw, (using a longer lever), you could easily lift your friend.
Forex leverage can be understood the same way. Your small deposit (you) is located at the end of a long financial lever. You can "lift" or control a much larger position in the market (your bigger friend). Obviously, the longer the lever (higher leverage ratio) you have, the more you will be able to control the same amount of effort (capital).
But here's the problem: if your friend jumps off their side as you are putting your weight down to push them up, you will hit the ground much harder than if you were on both sides of a lever. A leveraged position is the same; if the market moves against you, your losses have been amplified just like your prospective gains were.
Analogy 2: The Mortgage Example
When you buy a house, you usually don't pay the purchase price in cash. You put down a deposit (usually 10% - 20%) on the house and the bank lends you the rest to purchase the house. For example, if you buy a house for $500,000, and place a $100,000 down payment, you are using 5:1 leverage to buy the house.
If the value of the house goes to $550,000, you have earned $50,000 on an investment of $100,000 (a 50% return). If the value of the house goes to $450,000, you have lost $50,000 (also 50% of your down payment).
Leverage for forex works exactly the same way. Your margin is the down payment, and when you enter a leveraged position, your broker uses your margin to lend you the money to control a bigger position. When you calculate the profits and losses, they will be applied to the full size of the position, not just your down payment.
Analogy 3: The Business Rental
Consider this: you want to start a food truck business. Instead of buying a truck for $80,000, for $1,000/month you can rent one. This $1,000 rent allows you to control an $80,000 asset and generate thousands of dollars of revenue.
If you are making $5,000 profit/month from your food truck, you have made a 500% return on your $1,000 rental. If instead, you are failing and only making $500/month selling from the truck, you are losing $500/month on your $1,000 investment - a 50% loss.
The rental fee is similar to your margin requirement, and the total value of the truck is the equivalent of your leveraged "position" size - where you control something that was much more valuable than what you paid upfront. With leverage, you are increasing both your upside and your downside.
The Universal Truth
Now let´s look below at the underlying principle in all of the examples – leverage has the effect of multiplying both your risk and your rewards, equally. In other words in all three cases – seesaw, mortgage, business rental – you have the same idea! You can do much more with less capital invested, but you have a greater risk!
A Simple Exercise
Give this a try: Imagine you have $5,000 that you want to invest in a small local business. Without leverage, if you received a 10% growth in business you would receive a $500 profit. Now, imagine you could control a $50,000 business with the $5,000 (10:1 leverage) you received the 10% growth that provides you a $5,000 profit – but if you experienced a decline in business of 10% you would also incur a loss of $5,000 and potentially lose everything.
This is exactly how leverage works in forex trading! There is no magical money being made here! It is borrowed power that amplifies everything that you do good and bad. The trick is understanding how to use that power properly, remembering good risk management practices while having realistic expectations about the opportunity and danger that exists when you add leverage.
Benefits of Using Leverage: Maximize Capital Efficiency
If used responsibly, there are several reasons to leverage that explain why leverage has become a key character of modern forex trading. Let's take a moment to look at some of these benefits, and delve into the rationale behind using leverage with the smart traders.
Capital Efficiency and Economics of Access
The most blatant advantage of leverage is that it greatly lowers the economic threshold required to get into the forex market. Without leverage, you'd need significant capital to capitalize on even modest profits from the slight price perturbations that characterize the currency markets. In forex terms, a standard lot will require 100,000 units of the base currency – this is a pretty substantial capital investment for most retail traders.
With leverage, a trader with $5,000 can control the same position size as a trader with $500,000 without leverage. Leverage enhances equality of access to forex markets and enables still meaningful transaction engagement for traders, even as they start out with small capital.
Portfolio Diversification Benefits
As mentioned in the second section, leverage allows you to use more complex portfolio management strategies. By using leverage, rather than risking your entire capital in a single large position, you can allocate your risk amongst various currency pairs, whilst still managing large positions.
For example, if you had $10,000 with 50:1 leverage, you could hold EUR/USD, GBP/JPY, and AUD/CAD positions at $50,000 each (thereby risking $1500 in total margin) and your net risk in total would only be $3,000. Thus, you have diversified your portfolio as well as still being able to make your profits.
Leverage Means More Profit from Small Price Moves
The currency market moves in small increments (pips). The nature of the currency market means that these small price moves will not generate very much profit without significant leverage for a majority of traders. It is here where leverage changes the game, and you can turn minor price movements into serious profit potential.
To put this into perspective, consider the following:
-
Without leverage: 50 pip move on a $1,000 position in EUR/USD = about $5 dollar profit
-
With leverage of 100:1: 50 pip move on a $100,000 position in EUR/USD = $500 profit
This amplification effect may allow you to have substantial returns based on the natural volatility of the forex markets.
Flexibility in Position Sizing
Leverage has opened the door to a level of flexibility never before seen in the way you can structure your trade. Position sizing can be adjusted exactly to your confidence level, risk tolerance, market conditions, etc. This sort of micro differentiation allows you to have more complex trading rules, while still managing risk.
Professional traders use different amounts of leverage for different trades: for example, 20:1 for a high confidence set-up, and maybe 5:1 for something that is a little more on the speculative side. Without the factor of being able to trade using leverage, this flexibility does not exist: the only option is having huge amounts of cash tied up in one position, and risking additional cash to cover this position.
Capital Preservation for Opportunity
Leverage also gives you the ability to keep much more of your cash available for new opportunities. With leverage, you do not have to singularly tie up cash in a single position. You preserve your liquidity while still having significant positions in the market.
This knocking boat is worth your consideration in fast moving markets where new trading opportunities may occur with very little notice. The fact that you have capital available to you to use as new opportunities arise - or may even arise in cases where you would have to close a profitable position if you could not keep some of your capital aside - can be very appealing.
Professional Trading Strategies
A lot of advanced trading strategies utilize leverage as an important aspect of being effective. This is particularly true for arbitrage opportunities, carry trades and statistical arbitrage strategies; they would require large position sizes to realize meaningful returns after costs of transactions/time and/or spreads have been accounted for.
Institutional traders and hedge funds leverage as part of a sophisticated risk management or return strategy. Retail traders can also make use of similar strategies but on a smaller scale.
Hedging Capabilities
Leverage allows for easier and cheaper hedging strategies. Businesses with international exposure can hedge currency risk without using as much capital. Traders can also hedge existing positions or establish synthetic instruments by leveraging instruments.
The Professional Perspective
Successful professional traders see leverage not as a method for getting rich quick but as a capital efficiency tool. They combine moderate leverage (usually 10:1 to 30:1) and firm risk management rules to consistently grow their capital while managing capital preservation
The lesson here is that the major advantage of leverage is not simply bigger profits - it gives you a vehicle for deploying capital more efficiently while retaining the proper levels of diversification and risk management. When used with discipline, knowledge and risk management, leverage can be a force for creating sustainable wealth in forex markets.
Remember, these advantages can only be achieved through proper use of leverage. The same power that can enhance your profits will also compound your losses, meaning that education and risk management are critical factors in your success!
Risks of Leverage: How Losses Are Exacerbated Too
While leverage has many positive attributes, it is essential to realize that it is a double-edged sword. The same force that magnifies your profits will magnify your losses. Let's take a deeper look into the real risks and how they can affect your trading account.
The Bottom Line on Amplification
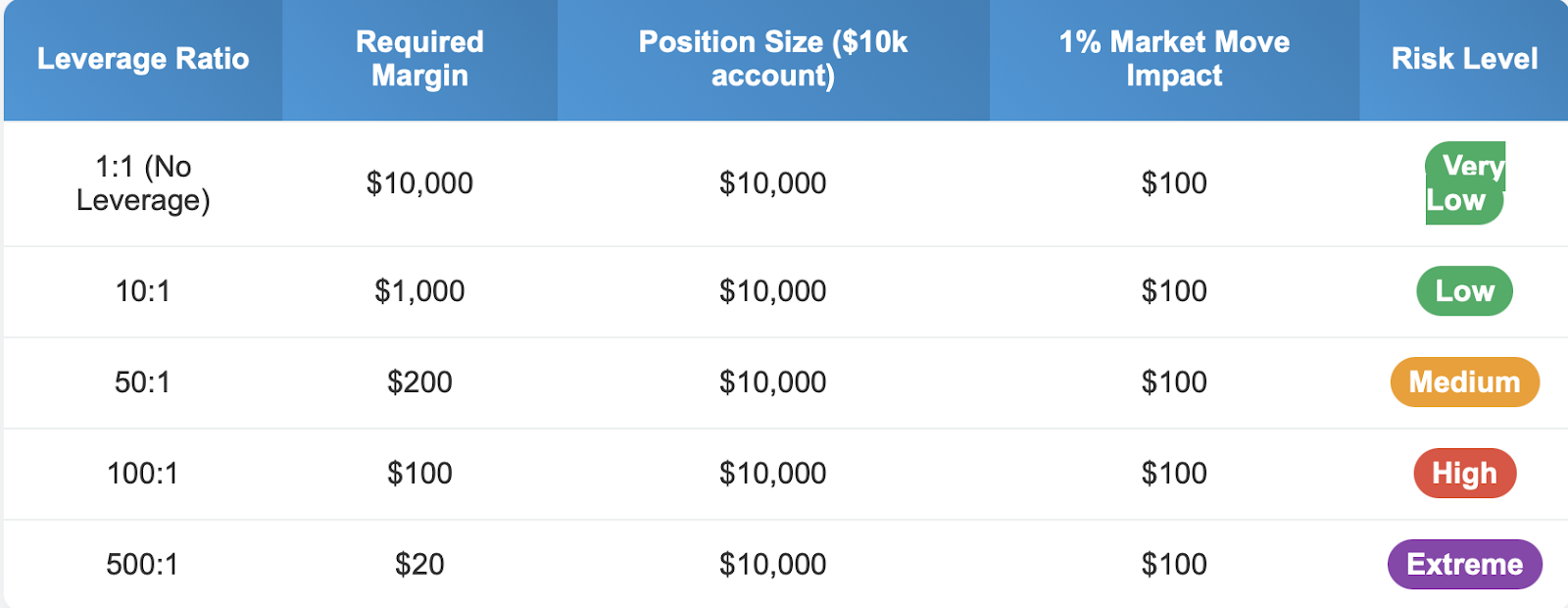
The main risk of leverage is purely mathematical; if you are using leverage, you are multiplying everything by some ratio. If you use 100:1 leverage, and the market moves 1% against you, you won’t lose 1% of your account; you will lose 100% of the margin you put down for that trade. This can lead to costly and rapidly overwhelming losses, if the trader isn't diligent.
Imagine two traders, with $10,000 trading accounts that are trading EUR/USD:
-
Trader A (No Leverage): Uses $10,000 to buy EUR/USD outright
-
5% market decline = $500 loss (5% of account)
-
Trader B (100:1 Leverage): Uses $1,000 margin to control a $100,000 position
-
5% market decline = $5,000 loss (50% of account)
Only two traders, with the same account size experience completely different results based on the use of leverage.
Margin Calls and Stop-outs
If your losses bring your account equity close to your available margin, brokers will issue margin calls asking for more funds. If you are unable to meet these calls, the broker will automatically close your positions to prevent you from losing more than your account value. Unfortunately, this forced exit often occurs at the worst possible time - when the market is moving against you quickly.
The process of margin calls works typically this way:
1. Margin Call Level: Usually triggered when your equity decreases to 100% of required margin
2. Stop-Out Level: Your positions are forcibly closed when equity decreases anywhere from 20%-50% of required margin
3. Forced Liquidation: Your positions are closed at current market prices, regardless of whether it is an appropriate time of exit
Volatility and News Events
Price movements in the forex market can be sudden and dramatic as a result of economic data releases, political events, or central bank decisions. These events can create gaps where a currency will jump drastically from one price to the next, skipping over your stop-loss order.
For instance, in January 2015, the Swiss National Bank made an unexpected announcement to drop the currency peg on the EUR/CHF. The Swiss franc proceeded to strengthen over 30% in a matter of minutes, leaving traders who had taken positions in EUR/CHF with high leverage with an instantaneous total account wipeout, regardless of their stop-loss.
The Psychological Trap
Poor decision-making frequently occurs because traders take on excessive leverage. As they see potential for large profits, traders may:
-
Forget risk management rules
-
Hold on to losing positions too long in hopes that they will reverse
-
Overtrade, taking too many positions at once
-
and/or use position sizes that are way too large for their account balance
This was the psychological side of leverage risk. The potential for loss with leverage can actually be much more dangerous than the mathematical risk because it leads to a compounding of poor decisions.
With overnight risk and weekend risk, you need to be aware of the forex market causing significant gaps when markets reopen after weekends or holidays. Holding leveraged positions, during overnight and weekend periods, puts you at gap risk where prices can move dramatically without escape unless you trade at very high volumes. Even if you have a stop-loss there is no guarantee it will protect you if there is a gap past your stop-loss level.
Correlation risk due to high leverage
When you use leverage on multiple positions, trades that appear to be diversified, may be leveraging a highly correlated trade at times of market stress. During the 2008 contagion crisis, many currency pairs that normally moved independently, began to all move together, which caused leveraged traders to have losing positions across their entire portfolio.
The vicious cycle of loss
Leverage can create a quick and nasty cycle of loss. If you lost half your account on a trade that was leveraged, you would need a 100% gain to break even for the account. This fact creates a math-based scenario in which it becomes embarrassing to overcome leveraged losses.
Real Life Statistics
Studies show;
-
Over time, 70-80% of retail forex traders will lose money
-
There is a strong correlation between higher use of leverage and account failures
-
The average lifespan of a highly leveraged retail trading account is 4 months or less.
Market Maker Risks
Some brokers may use your high leverage against you by employing a practice called stop-loss hunting or widening spreads during volatile times. With high leverage, these practices can quickly devastate your account.
The Margin of Error
High leverage also reduces your margin of error considerably. A trader using 10:1 leverage can withstand a 10% adverse move before serious issues arise, whereas, with 100:1 leverage, a trader with 1% will encounter the same issues.
Protection Strategies
The first step in managing risks is knowing what they are. Good traders protect themselves using:
-
Appropriate position size (risking only 1-2% per trade)
-
Strict stop-losses before entering trades
-
Not taking excessive leverage ratios, which can often lead to conversation; but use caution when discussing leverage in front of regulated traders, they might not know what position sizing is.
-
Adequate minimum account reserves
-
Never add to losing leveraged positions
The key messaging here is that the risk of leverage is not theoretical - it happens daily and can destroy trading accounts quickly. That said, if you understand the risk and follow some simple strategies, you can manage and reduce risk in trading. You can reap the benefits of leverage and still protect your capital.
How to Trade Leverage Safely: Useful Tips
Knowing how to trade leverage safely is one of the important differences between a trader who can trade for a long time and a trader who blows out their account. In this article, I will go through some proven techniques and methods to leverage your trades in a prudent future thinking way instead of a reckless manner.
Start with your risk profile
Before you can even think about any leverage ratio. You need to know your risk profile. You must ask yourself "What percent of my entire account am I comfortable losing on one trade?" Most professional traders use a position risk rule between 1-2 percent of their total account balance risked per position.
Once you know your risk profile you can use it and work backwards to know how much leverage you are using:
-
If you want to risk 2 percent (or $200) trading on a $10,000 account
-
And your stop loss is 50 pips away
-
Then you are only going to need to match a trade size with a big stop, of when 50 pips = $200 loss
By this you will determine how much leverage on that trade you can take
The Position Sizing Formula
You can use this formula for all your trades:
Position Size = (Account Balance x Risk %) / ((Stop Loss in pips) x (Pip Value))
In this example:
-
Account Balance = $5,000
-
Risk per trade = 2% ($100)
-
Stop loss distance = 40 pips
-
Pip value for your lot size = $1 per pip (mini lot)
Position size = $100 / (40 * $1) = 2.5 mini lots maximum
Let Market Conditions determine your Leverage
Vary your leverage depending on current market volatility:
Low Volatility Environments:
-
Currency pairs trading within narrow ranges and small pullbacks
-
Use leverage within moderation (20:1 to 50:1)
-
Stop-losses will be smaller
High Volatility Environments:
-
Major news announcements, central bank monetary policy
-
Lower leverage (5:1 or 10:1)
-
Wider stop-losses result in smaller positions
Timeframe Leverage Adjustments
There are many factors that can affect your approach to leverage during different trading sessions. For example:
-
Asian Session: There is generally lower volatility and I would use moderate leverage
-
London Session: Higher volatility and therefore, reduce leverage
-
New York Session: Highest volatility and I would use minimal leverage
-
Overlap periods: Extreme caution with regards to leverage because of increased volatility from London and New York Sessions colliding
The Pyramid Strategy
Instead of opening one large leveraged position, consider opening leveraged positions in stages, or using a pyramid method:
-
Open Position: 25% of the position you want to take
-
If you have 25% a move in your favor, add an additional @25% more
-
If you have had a considerable move in your favor, add another at 50% of your initial position
-
Move Stops to protect profits as you add to your positions
The benefit to pyramid trading is that you are minimizing the initial risk of an one big mistake but still have considerable profits if your analysis is correct.
Leverage Guidelines by Currency Pair
Different currency pairs attract different leverage guidance:
Major Pairs (EUR/USD, GBP/USD, USD/JPY):
-
Generally more liquid and predictable.
-
Moderate max leverage (30:1 to 50:1).
Minor Pairs (EUR/GBP, AUD/JPY):
-
Often more volatile and less liquid,
-
Use lower leverage (10:1 to 20:1).
Exotic Pairs (USD/TRY, EUR/ZAR):
-
Highly volatile and often unpredictable.
-
Very little leverage suggested (5:1 to 10:1).
-
Stop-Loss as a Safety Net
You should never enter a leveraged position without an established stop-loss. The steps to take are as follows:
-
Prior to the Entry: Know where you plan to exit before opening the trade.
-
Based on Technical Levels: Support/Resistance levels, not arbitrary percentages %.
-
Accommodate Spreads: Always account for where the stop-loss is located relative to the bid-ask spread.
-
Do not Move Stops: Never adjust a stop-loss further from your entry point.
Utilize Laddering Strategy
Define different leverage levels for different types of trades:
-
High Confidence Trades (20:1 to 30:1):
-
Clear technical setups
-
Confluence of multiple indicators
-
Strong fundamental backing for the trade
Medium Confidence Trades (10:1 to 15:1):
-
Decent setup with uncertainty
-
Fundamentals are mixed
Experimental Trades (5:1 to 10:1):
-
Testing different strategies
-
Market conditions are uncertain
-
Learning trades
Regular Review and Modify
-
Carefully keep a record of every trade in a trading journal so you can track:
-
At what level you leveraged each trade, % of risk taken on each trade
-
What the outcome was and what you ultimately learned from it
To observe and identify patterns, review your journal on a monthly basis:
-
Did you lose primarily on trades with high leverage?
-
Did you mostly make better decisions and outcomes when your leverage was lower?
-
At which levels of leverage does you trading style appear to thrive?
The 50% Rule
A simple risk management tool. If any single trade reaches 50% of your original maximum loss size, immediate halt to leverage on your next trade, until you figure out what went wrong. Why? So you do not let a small problem escalate into a problem!
Emergency Rules
Set some guidelines to protect yourself in extreme situations including:
-
If your account falls 20% of original starting balance, cut teh maximum leverage to 1/2 original trade size
-
If you have three continuing losses in a row on leveraged trades, take a holiday
-
If you have a major news event approaching, think about closing or reducing leveraged trades.
The Professional Mindset
Keep in mind that professional traders will use leverage, and they see leverage as a tool that helps create precision rather than a path to rapid wealth. Successful professional traders know the value of capital risk management and controlling their trading risk.
They are concerned with small, consistent, incremental returns over time and protecting their capital at all costs by using only the necessary amount of leverage at their disposal, and by treating their returns as part of a larger statistical edge.
Smart leverage use is all about identifying the degree of risk within the leverage by finding the ultimate balance between the profit potential and the risk that traders should take into consideration.
Smart leverage will take discipline, planning and regular review or the action of revising their plan or strategy based on market conditions and their personal performance.
Using maximum leverage is not the goal, using optimal leverage, that reflects your specific situation and objectives, is the aim.
Common Myths & Questions
Let's tackle the commonest myths and questions about leverage in forex, to make sure you have a proper and factual understanding of this powerful trading tool.
Q1: Is higher leverage always good to make profits?
Myth: "If 50:1 leverage is good, than 500:1 leverage must be ten times better!"
Reality: Higher leverage does not mean higher profits; it simply means higher risk. Your ability to profit is based on your position size and market movement, not your leverage ratio. A trader who is using 10:1 leverage with proper risk management may profit more than someone using 500:1 leverage in a reckless manner.
Myth: There is no one best leverage, it will depend on the trader's experience level, risk tolerance, and market conditions. All successful professional traders use moderate levels of leverage (10:1 pockets to 50:1), and always with strict risk management.
Q2: Are margin and leverage the same thing?
Myth: "Margin and leverage are just two different words that mean the same thing."
Reality: Please note that they are similar but different.
-
Margin: The actual deposited currency that acts as your collateral (for example, $1000)
-
Leverage: The ratio that determines how much money you can control (i.e. 100:1)
-
Position Size: The result of margin × leverage (i.e. $100,000)
You can think of margin as the initial deposit and leverage as the multiplier that determines what you are controlling with that deposit.
Q3: Is it possible to lose more money than I have in my account?
Myth: Possible. "Leveraging means I can owe money to my broker."
Reality: Most regulated brokers provide negative balance protection, meaning you can't lose more than what you have in your account. However, not every broker provides this protection, and not all extreme market conditions will apply it.
Important Note: In extreme market conditions such as a crash, or if you trade with an unregulated brokerage, you may be liable for a negative balance. Make sure you check your brokerage negative balance policy.
Q4: Is using leverage going to cost me money?
Myth: No. "More leverage = higher trading costs."
Reality: This is usually not the case with leverage. Leverage itself usually does not cost anything. However, the assets you trade with leverage may incur:
-
Overnight financing costs (swap rates) if you keep your position open for longer than one day
-
Standard commissions and spreads based on the size of your position
-
Some brokers may even charge margin interest on leverage
-
The leverage ratio itself does not typically charge any fees directly to trading.
Q5: Do lower leverage levels always keep me safer?
Myth: "If I traded with 10:1 leverage instead of 100:1, my trade will be at zero risk."
Reality: Leverage doesn't create risk – poor risk management is. You can lose money on lower leverage if you:
-
Do not use stop-losses
-
Risk too much of your account on single trades
-
Go against the market without a trading plan
The Key: Risk isn't from only leverage ratio, but from position sizing and proper risk management.
Q6: Can I change my leverage ratio at any time?
Myth: "I can modify my leverage while an open trade is in play."
Reality: Most brokers will allow you to modify the maximum leverage ratio for your account but it usually mean:
-
It doesn't apply to current open positions
-
It only applies for future positions
-
It may not be usable unless you close ever position in your account
Best Practice: Set the proper level of leverage before taking any trades, rather than try to make changes in the middle of a trade.
Q7: Is leverage gambling?
Myth: "All leverage is is gambling with borrowed money."
Reality: Leverage is just a tool. A tool that can be used effectively or carelessly:
Gambling: Using maximum leverage with no analysis, risk management, or strategy
Professional Trading: Using moderate leverage with analysis, stop-losses, and proper position sizing
The difference: Education, planning, and risk management is what sets leverage use by professionals from gambling.
Q8: Do I need high leverage to make good money in forex?
Myth: "There is no need to use forex unless you have high leverage, otherwise your profits will be so small it doesn't matter."
Reality: Successful traders focus on percentage returns not how many dollars they are making. A 2% return each month will compound over a longer period of time, regardless of which leverage you decide to use.
Example:
-
$10,000 funding account earning 2% monthly = in 5 years, the account will turn $10,000 into $26,973
-
All this can be achieved using moderate leverage and good risk management.
Q9: Does my broker protect me from large losses automatically?
Myth: "The margin call structure of my broker eliminates my risk of major losses."
Reality: Margin calls and stop outs provide some protection; however:
-
Markets may gap past your stop-loss levels
-
Excessive volatility may produce slippage
-
A fault in the system may occur during a critical time.
Your Responsibility: Never rely solely on broker protection measures and always use your own stop-loss system and risk management options.
Q10: Should beginner traders avoid leverage?
Myth: "That's just common sense! New traders should never use leverage until they are experts."
Reality: It is not necessary to avoid it altogether, but beginner traders should:
-
Start using very low leverage, maybe 5:1 to 10:1, to begin with
-
Focus more on learning proper risk management practices first and foremost
-
Use demo accounts to practice extensively
-
Only increase leverage as a trader, after you can prove consistent profits with low leverage.
The Bottom Line: The emphasis should be on education and being progressive rather than completely avoiding leverage trading.
Key Takeaways For Avoiding Common Mistakes
-
Leverage amplifies gains and losses equally
-
Higher levels of leverage do not mean higher levels of profit automatically
-
Risk management is much more important than leverage ratios
-
Understanding comes before exploiting higher levels of leverage
-
You should demo trade before you live trade levered positions
Just keep this in mind, the most expensive mistakes in forex are often a result of misunderstanding leverage. Before putting your real money at risk, take the time to make sure you understand all of these concepts, and don't ever be afraid to ask questions or seek clarification if you're unsure about something!
Conclusion, and Call to Action
Over the course of this guide on leveraging (for forex), we have examined leverage from every angle possible: the mechanics, benefits, risks and most importantly how to use it wisely. Let's review the important aspects that you will all have to rely on in order to conduct leveraged trading successfully.
The Core Understanding
Leverage is a powerful amplifier that magnifies your potential profit and potential loss equally. It is not a path to riches by default, nor is it dangerous in itself. Like every other professional tool you need to employ, leverage is dependent upon how well and responsibly you use it.
These are the basic truths worth bearing in mind:
-
Leverage itself does not constitute a risk; it is other poor management of that risk
-
Higher ratios of leverage don't equate automatically with higher profits
-
Your position-sizing and stop-loss strategies far outweigh leverage
-
Successful traders use leverage as one more tool in their set of precision dial-tools, not as a mechanism for gambling
The Smart Trader's Way
Successful, professional traders assess their use of leverage in terms of the following:
-
More clearly defined risk tolerance, usually between 1-2% of the total account balance
-
Position-sizing formulas are incorporated instead of gut sense
-
Dynamically adjusted consider volatility levels and market climate
-
Apply modest leverage in conjunction with strict stop-loss discipline
-
Detailed record keeping of both wins and losses to learn
-
Focus on general percentage gains rather than home run hits
Next Steps
Knowledge without execution is just theory. A pragmatic framework for putting what you've learned into real aspects:
Phase 1: Developing Groundwork(Weeks 1-2)- Start a demo trading account and practice the concepts of leverage where there is zero financial risk involved. Things to focus on:
-
learning to work out position sizes with the formulas we have discussed
-
using technical analysis to set reasonable stop-losses
-
practicing leverage ratios and try to see the effects
-
practice with the major currency pairs first (i.e. EUR/USD, GBP/USD, USD/JPY).
Phase 2: Skill Development (weeks 3-8) Once you're comfortable with the mechanics, start developing your trading strategy:
-
What your preferred style of trading is (scalping, day trading, swing trading etc).
-
What your comfort level and optimal levels of leverage
-
Practice position building in pyramids
-
Keep a thorough trading journal and keep track of your leverage decisions.
Phase 3: Live trading transition (weeks 9 +): When you're consistently profitable on demo accounts:
-
Open a very small live account ($500-$1,000)
-
Use less leverage than you demonstrated in the demo practice (aim for half or lower).
-
Only trade 1-2 trades for the first 1-2 weeks.
-
Increase orders only when you have proven consistency (forward tests) and can increase position sizes gradually.
Selecting the Appropriate Broker
Your choice of broker is your most important decision in order to be successful using leverage, so look for the following:
Regulated: Confirmed licensing and regulation
Negative Balance Protection: Protection so you will not owe more than what you deposit
Competitive spreads: The smaller the cost, the easier it is to be profitable
Reliable execution: No slippage when you really need it
Educational material: Availability of ongoing education
Flexible leverage options: The ability to change leverage as you grow
Risk Management Checklist
Before you make any leveraged trade, make sure you have done the following:
-
Calculated your position size based on your account balance and risk percentage
-
Determined the stop-loss level and placed it before entry
-
Your risk-reward ratio is minimally 1:2 (risk $1 in order to potentially make $2)
-
Total account risk based on all open positions is no greater than 5%
-
You understand the rationale and technical reasons for making the trade
-
Market conditions allow for your leveraged level
Continuous Learning Path
Leveraging mastery requires ongoing education:
Immediate Steps:
-
Read central bank communications to keep ahead of what will drive the market
-
Follow economic calendars to understand the best time to be involved in trading
-
Review how successful traders approach leveraging and risk management
-
Participate in communities to engage in ongoing discussions and education
Long-term Education:
-
Take acceptable higher-level courses on risk management, risk theory, and the risk subjects of portfolio theory
-
Educate yourself on behavioural finance to understand the psychological pitfalls of trading
-
Educate yourself on correlations so you can truly diversify your leveraged position
-
Educate yourself on the algorithmic approach and their concepts so you can systematically leverage
Danger Signs to Be Mindful Of
Be aware of these danger signs that indicate you are not using leverage properly:
-
Always risking more than 2% per trade
-
Moving stop-losses away from entry points to avoid taking losses for trades
-
Increasing position sizes as each 'loser brings you closer to a 'winner' when you are losing
-
Feeling anxious about open positions and/or not able to sleep/rest
-
Making trading decisions based on your account balance situation and or needs, NOT based on analysis of the market.
-
If you are experiencing any of these behaviours you need to stop with the leverage immediately and reassess.
The BTCDana Advantage
Are you ready to put your leverage knowledge to good use? The BTCDana environment is perfect for both learning and developing expertise as a leveraged trader.
As a demo account user, you will have:
-
A risk-free environment in which to practice all the leverage concepts with zero consequences
-
A market closest to the real market you will find with 100% fake money
-
Full access to the trading platforms and tools
-
Unlimited time to brainstorm, develop, and test your strategies
As a live account user, you will have:
-
Flexible leverage depending on your trading experience and knowledge
-
Some of the most competitive spreads and costs for trading major currencies
-
Advanced risk management tools
-
Customer support 24/7 if you need help with the complexity of leverage trading
-
All the educational content and market analysis will continue in the live account
Plus, in addition:
-
Interactive webinars, and/or live-stream webinars on leverage and risk management strategies
-
Your very own personal trading manager will assist you with learning
-
You will receive continuing market updates and trading ideas
-
You will have access to community forums to learn from each other, and to share knowledge with fellow traders
Take Action Today
The difference between traders who succeed with leverage and those who fail isn't luck – it's preparation, education, and disciplined execution. You now have the knowledge foundation. The next step is controlled, careful practice.
Take Those Next Steps:
-
Open your BTCDana demo account now and practice leverage concepts with no risk
-
Download the leverage calculator and simplify the calculations needed for position sizing
-
Enroll in our webinar series to continue learning and ask questions about your trading
-
Follow the daily market analysis to learn how professional traders approach leveraged trading
And always remember, everyone who is an expert was once a beginner and the key is getting started with the right information, proper education, and realistic expectations. Leverage can be a powerful partner in your journey to building forex trading success - but only when you know what you are doing and have the ability to use leverage effectively.
Your forex trading journey starts with one step. Take that step now, armed with the information and tools you need to drive safely and profitably with leverage.
Are you ready to take that step? Go to BTCDana.com, and open your demo account so you can practice everything you have learned. Your future self will thank you for spending the time learning about leverage properly before you risk your real capital.
The forex market rewards those who possess both knowledge and applied discipline. You have the knowledge - what is left is the discipline in terms of practice and experience. Build both starting today.